Martín-Ramírez R, González-Nicolás MÁ, Álvarez-Tosco K, Machín F, Ávila J, Morales M, Lázaro A, Martín-Vasallo P.Cells. 2025 Aug 20;14(16):1294. doi: 10.3390/cells14161294.
Abstract
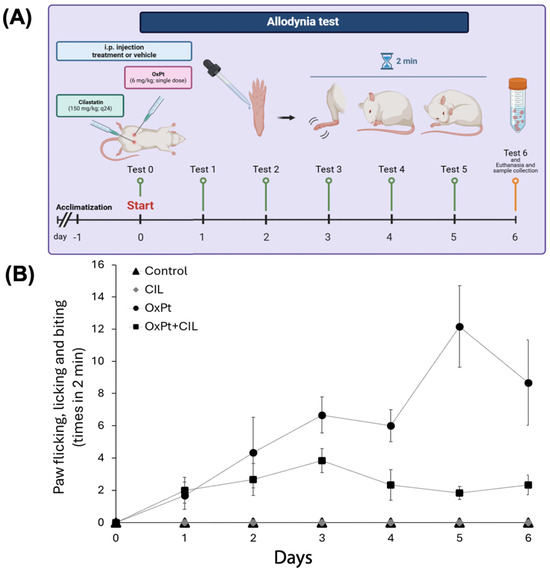
Oxaliplatin-induced peripheral neurotoxicity (OIPN) represents a major challenge in cancer therapy, characterized by dorsal root ganglia (DRG) inflammation and disruption of neuro-glio-vascular unit function. In this study, we investigated the involvement of the scaffold protein IQ Motif Containing GTPase Activating Protein 1 (IQGAP1) and dehydropeptidase-1 (DPEP1) in the DRG response to oxaliplatin (OxPt) and the modulatory effect of cilastatin. Behavioral assessment showed a robust nocifensive response to cold stimuli in OxPt-treated rats, attenuated by cilastatin co-treatment. Our confocal study revealed different cellular and subcellular expression patterns of IQGAP1 and DPEP1 in neurons, glia, and endothelial cells, where both signals overlap approximately one-third. OxPt enhanced cytosolic aggregation of IQGAP1 in neurons and upregulation of signal in glia, accompanied by co-expression of TNFα and IL-6, indicating involvement in the inflammatory process. DPEP1 showed altered subcellular distribution in OxPt-treated animals, suggesting a potential role in the inflammatory cascade. Notably, IQGAP1 expression was diminished in endothelial membranes under OxPt, while cilastatin preserved endothelial IQGAP1-CD31 colocalization, suggesting partial restoration of blood-nerve barrier integrity. These findings identify IQGAP1 and DPEP1 as key players in DRG inflammation and position cilastatin as a promising modulator of OIPN through neuro-glio-vascular stabilization.
Keywords: DRG-inflammation; IQGAP1; allodynia; cilastatin; dehydropeptidase-1; dorsal root ganglion (DRG); neurotoxicity; oxaliplatin; peripheral neuropathy.